Install Openssh Windows Vista
Installing OpenSSHOpenSSH is what we’ll be using, so if you don’t have it installed, find Cygwin’s setup.exe file and run it.You can keep all of the same defaults as when you originally set up Cygwin. On the package selection screen, search for “open” and look under the “Net” menu.You’ll see a package called “openssh”. Click under the “New” column, where it says “Skip” until you see an X appear in the “Bin?” column. Look at the previous screenshot for where to click if you’re confused. Hit “Next” and finish up the rest of the setup process, just like you did last time.
Configuring OpenSSH in CygwinUnlike in most Linux distros, OpenSSH won’t automatically configure itself to run and just work. We need to perform a few easy steps. First, right-click your Cygwin shortcut, and click on “Run as administrator”:This will make sure we have the proper privileges for everything. You’ll see an empty Cygwin window come up.Enter the following command:ssh-host-configYou’ll see the script generate some default files, and then you’ll be prompted for whether or not you want to enable “Privilege Separation.” It’s on by default in standard installations of OpenSSH on other systems, so go ahead and say “yes” to the prompt.You’ll be prompted to create a new account with special privileges.
Select “yes” and the script will continue. Next, you’ll be asked if you want sshd to run as a service. This will allow you to get SSH access regardless of whether or not Cygwin is currently running, which is what we want. Go ahead and hit “yes” to continue.Next, you’ll be asked to enter a value for the daemon.
Enter the following:ntsecYou’ll see the script give you some information on your system and then it will ask you to create a privileged account with the default username “cygserver”. The default works well, so type “no” when it asks you if you want to use a different account name, although you can change this if you really like.Of course, you’ll have to enter a password for this account as well.Cygwin will show you your password in plain text for verification, so be sure you’re in a secure place. You’ll see some extra info come up and if all’s well, you’ll get a message that says it successfully completed.You can either restart, or enter the following command to start the sshd service:net start sshdNow, you can type “exit” to close this Cygwin instance. User Configuration of SSHNext, we’ll create the appropriate SSH keys for your user account.
Open up Cygwin normally, and enter the following command:ssh-user-configYou’ll be asked to create specific keys for your user account, so use what you need. I went ahead and said “no” to the first question, and “yes” to the second.SSH2 is more secure, so that’s what I recommend to you. After entering a password, you’ll be asked if you want to use that ID to access your machine. Type “yes”.Next, you’ll be asked to create an SSH2 DSA ID file, if you want to use password-less access. I declined at this step.That’s it! You’re all configured.
If you want to test your configuration really quickly, enter the following command in your Cygwin window:ssh –v localhostThe –v option stands for “verbose” and gives you all of the details of the process. You’ll be asked if you want to continue connecting, so enter “yes” and then enter your password at the prompt.
Remember that when you enter your username, it is case-sensitive!If everything worked out well, you’ll see a normal bash prompt. Minor IssuesIf you find yourself stuck at any of the configuration steps, make sure that the Windows User Account you’re running has Administrative access.
You may get weird errors if you try to run the host configuration as a normal user, so make sure you run Cygwin with admin privileges during that step. If, when you exit, you get a prompt about leaving your batch jobs running, you can hit “no” to terminate them.Lastly, if you test SSH access from another machine and get an error, make sure that your firewall isn’t blocking access to port 22 (or 23 if you’re using SFTP).This works extremely well if you like the ability to get SSH/SFTP access to your files on a Windows 7 machine and you also want a familiar shell to do that with. Cygwin mounts Windows drives to “/cygdrive/driveletter” in case you were wondering.;-).
The ssh server is an emulation of the UNIX environment and OpenSSH for Windows, by Redhat, called cygwin.The file system on your target machine should be journalled (e.g. NTFS) because FAT file system has bugs in file access. Thanks to Jared Kilgour for above $USERNAME variable substitution.Thanks to Justin Kerk for the tip on quotes around $USERNAME to allow for spaces in username.Thanks to Ron Dozier of University of Delaware for the Unix.login tweak.Windows XP SP2 and SP3: open the Windows Firewall to allow TCP port 22 throughClick Start.Control Panel.Security Centre.Manage Security Settings for WindowsFirewall.Exceptions tab.Add Port.' Name of port' is ssh 'Port number' is 22(check the 'TCP' checkbox)(Thanks to Stefano of Sardegna, Italy for hisWindows Firewall reminder)If you don't have sufficient privileges to open port 22 above, possible dueto a group policy or other reasons,you can create an exception for SSHD.Click Start.
Control Panel.Security Center. Windows Firewall.select the'Exception' tab.Click 'Add Program' button. Browse to c:cygwinbinsshd.exe(Thanks to Thomas Johnson for this work around)If you previously used Windows XPSP1and installed sshd service, then upgraded to Windows XP SP2,The upgrade disables the sshd service and deletes the CYGWIN environment variable.Re-enter the environment variables and path.Click Start.Control Panel.Security Centre.Manage Security Settings for WindowsFirewall.Exceptions tab.Add Port.' Name of port' is ssh 'Port number' is 22 (check the 'TCP' checkbox)(Thanks to Chris Davitt of New Zealandfor this SP1 to SP2 problem)Multiple Windows usersCreate other Windows users using the Control Panel. Installing the Cygwin SSH daemonHow to setup the secure shell daemon on a Windows 2003 server Note: This set of instructions has worked for me atour institution.
You should read /usr/share/doc/Cygwin/openssh.README afterinstalling cygwin and check the if you encounter problems.Installing and Testing cygwin. Create the destination folder (C:cygwin or D:cygwin as appropriate).Default permissions will be for administrators and SYSTEM only. AddSERVERUsers with modify control to the list. These permissions willbe inherited to the rest of the folder as it is populated. Create a directory to locally store the cygwin packages e.g.C:tempcygwinarchive.
Open a browser window to the following URLand save the installation file setup.exe to the archive directory justcreated (C:tempcygwinarchive in this example). Double click on the downloaded cygwin setup program.
The current version is2.510.2.2 (February 3rd, 2006). Click 'Next' and answer the prompts:. Leave default 'install from internet'. Install to root directory c:cygwin.
leave default 'install for all users'. leave default text file type 'unix / binary'. Set local package directory to c:tempcygwinarchive (the directorycreated in the previous step).
This should be the default. Leave the default 'direct connection'.
Select a mirror (any of the ones with starting with the name). The package list will be downloaded. The 'Select Packages' window can be stretched. Click on the plussign to expand the categories. Install at least the following list ofpackages. From Admin, select all packages. From Archive, select unzip and zip packages.
From Base, leave the default, select all packages. From Doc, leave the default, man and 'cygwin doc' packages. From Editors, select vim package. From Net, select openssh (openssl will get checked automatically),rsync and tcpwrappers packages. When you've selected these packages, click 'Next'.
The installationtells you which packages it is installing as it progresses. Uncheck 'Create desktop icon'. Leave default 'Add to start menu'.Click 'Finish'.
A post install script runs a few final commands. Then you should seea message saying 'Installation complete'. Click 'OK'. Edit C:cygwincygwin.bat.
Make sure it contains these lines - youwill need to add the line setting the CYGWIN environment variable.@echo offset CYGWIN=binmode tty ntsecC:chdir cygwinbinbash -login -i. Test cygwin to make sure it works. Start, Programs, CygnusSolutions, Cygwin Bash Shell - should get a command window with aprompt saying 'Administrator@servername'.
This is a bash shell andyou can use unix or DOS / NT type commands e.g. 'ls /bin' to see the cygwin bin directory.
'dir c:' to see the contents of the C: directoryType 'control d' or 'logout' to exit the shell. If you get a message saying 'cannot create /home/userid', runthis command from the cygwin window 'mkpasswd -l /etc/passwd'. While you're in the cygwin shell window, run this command to changethe mount prefix from '/cygdrive' to '/'. You should logout and back inagain after running this command in order to reset your PATH environmentvariable properly.mount -s -change-cygdrive-prefix /.
Also, create a home directory where you can place user startup files.The default location is the 'Documents and Settings' folder. Creating a/home directory and using the -p switch to assign the home directorywhen adding a new user keeps all the cygwin files under the c:cygwindirectory.mkdir -p /homeInstalling the SSH daemon service. From a cygwin prompt (Start, All Programs, Cygwin?), run ssh-host-configto create the service, set up the ssh host keys and create the sshdconfigfile in /etc/. Note that 2 local users are created, one called sshd to handleprivilege separation and one that is required on Windows 2003 calledsshdserver that runs the service in order to use public key authentication.You should see output like this:$ ssh-host-configGenerating /etc/sshhostkeyGenerating /etc/sshhostrsakeyGenerating /etc/sshhostdsakeyOverwrite existing /etc/sshconfig file?
(yes/no) yesGenerating /etc/sshconfig fileOverwrite existing /etc/sshdconfig file? (yes/no) yesPrivilege separation is set to yes by default since OpenSSH 3.3.However, this requires a non-privileged account called 'sshd'.For more info on privilege separation read/usr/share/doc/openssh/README.privsep.Should privilege separation be used? (yes/no) yesWarning: The following function requires administrator privileges!Should this script create a local user 'sshd' on this machine?
(yes/no) yesGenerating /etc/sshdconfig fileAdded ssh to C:WINDOWSsystem32driversetcservicesWarning: The following functions require administrator privileges!Do you want to install sshd as service?(Say 'no' if it's already installed as service) (yes/no) yesYou appear to be running Windows 2003 Server or later. On 2003 andlater systems, it's not possible to use the LocalSystem accountif sshd should allow passwordless logon (e. Public key authentication).If you want to enable that functionality, it's required to create a newaccount 'sshdserver' with special privileges, which is then used to runthe sshd service under.Should this script create a new local account 'sshdserver' which hasthe required privileges? (yes/no) yesPlease enter a password for new user 'sshdserver'.
Please be sure thatthis password matches the password rules given on your system.Entering no password will exit the configuration. PASSWORD=xxxxxxxUser 'sshdserver' has been created with password 'xxxxxxxx'.If you change the password, please keep in mind to change the passwordfor the sshd service, too.Also keep in mind that the user sshdserver needs read permissions on allusers'.ssh/authorizedkeys file to allow public key authentication forthese users! (Re-)running ssh-user-config for each user will set therequired permissions correctly.Which value should the environment variable CYGWIN have whensshd starts? It's recommended to set at least 'ntsec' to beable to change user context without password.Default is 'ntsec'.
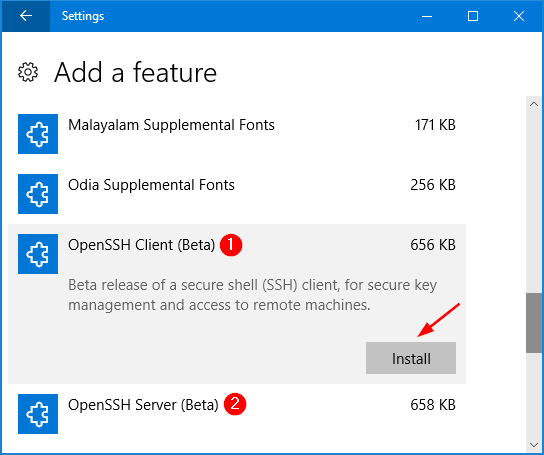
Install Openssh Server Windows 10
CYGWIN=binmode ntsec ttyThe service has been installed under sshdserver account.To start the service, call net start sshd' or cygrunsrv -S sshd'.Host configuration finished. Have fun!. You can start the service from the services MMC panel, or using either ofthe commands listed above ('net start sshd' or 'cygrunsrv -S sshd').Generating public/private SSH keys for a user.
If you need to generate ssh public and private keys for a user on thismachine who will be uploading data or logging in to a remote machine, youwill need to carry out this step. Sign on as the user who needs the keyscreated. They will automatically be in their home directory. Runssh-user-config to setup the ssh keys. Create only an SSH2 RSA identity(use a null passphrase - just press return). Output should be similar to this:cygwinadmin@HICKORY $ ssh-user-configShall I create an SSH1 RSA identity file for you? (yes/no) noShall I create an SSH2 RSA identity file for you?
(yes/no) (yes/no) yesGenerating /home/pswander/.ssh/idrsaEnter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Press ENTEREnter same passphrase again: Press ENTERDo you want to use this identity to login to this machine? (yes/no) yesShall I create an SSH2 DSA identity file for you? (yes/no) (yes/no) noConfiguration finished. Have fun!. Update the file /home/userid/.ssh/authorizedkeys with any public keysfrom other users who you wish to be able to connect to this user's account.Refer to for more information.